Briefly Describe the Three Dimensional Structure of Dna
So first of all theyre anti parallel meaning one will be going from this reform to five prime. We discuss three emerging approaches to analyze 3C-based datasets.

Protein Structure Introduction To Chemistry
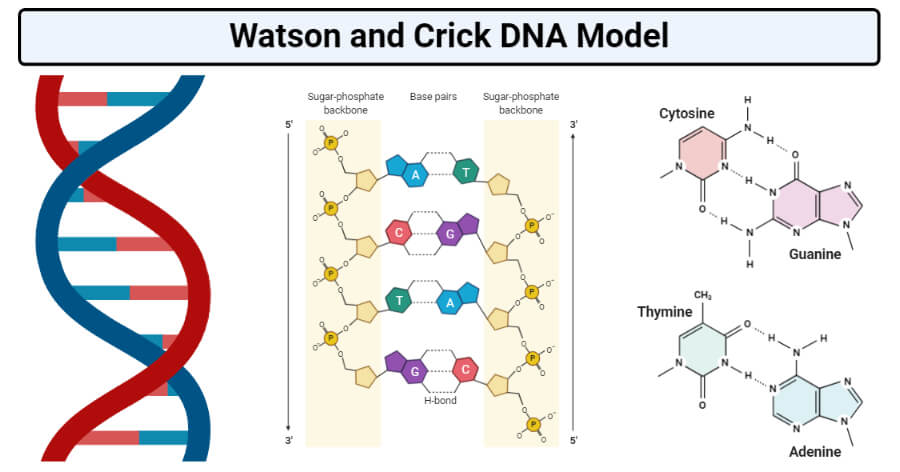
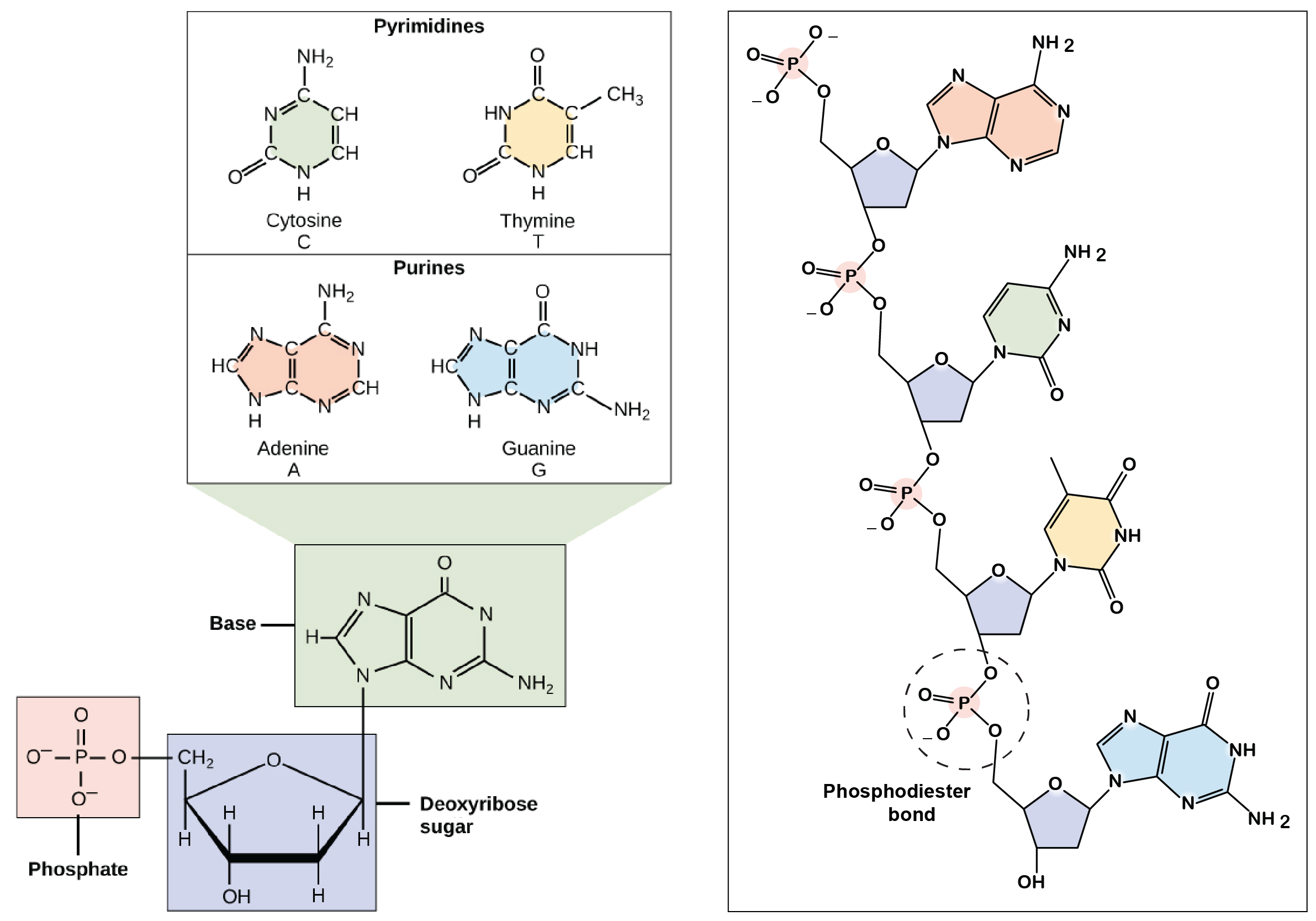
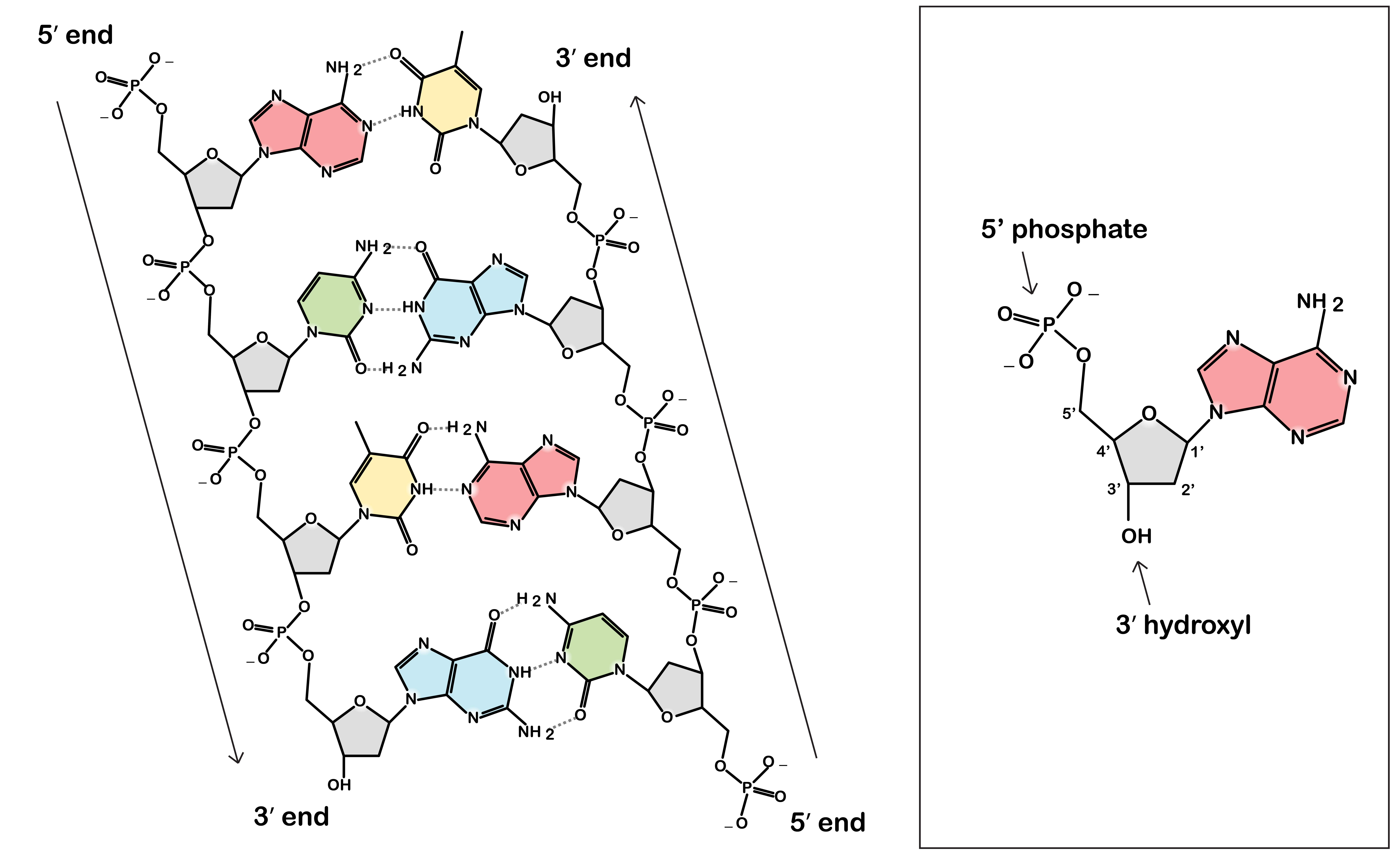
Two strands of DNA that are anti-parallel run opposite directions form 5 to 3like a divided highway form a double helix structure around an imaginary axis.
. Replicating photograph 51 How do we know that the DNA molecule is a double helix. This is much like what a strand of DNA looks like. The structure is called a double helix.
1B DNA is a double helix formed of two polynucleotide strands twisted in right handed fashion. DNA is essentially made of. Briefly describe expanding nucleotide repeats.
Watson and Francis H. Arises from natural changes in DNA structure or from errors in replication. DNA has a double helix structure.
Explain the relationships among chromatin. The three-dimensional structure of DNAthe double helixarises from the chemical and structural features of its two polynucleotide chains. Answered 5 years ago.
Distorting the three-dimensional structure of the helix and causing single-nucleotide insertions and deletions in replication. In your answer include Watson-Crick base pairing and Mg2 Transcription. Discuss other three-dimensional structures that DNA may adopt and how these structures may affect its biological functionIntroduction Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA contains genetic instruction that are critical for the development and function of all living things.
Here we briefly describe the main experimental approaches and then describe in more depth recently developed analytical computational and modeling approaches for analysis of comprehensive chromatin interaction datasets. Breaks in complementary regions can result in loops and bulges that together with the helical regions can generate a precise three-dimensional structure. B DNA A DNA and Z DNA.
Briefly describe the effects each of these enzymes has on the structure or topology of a DNA molecule and explain the function if. There are three conformation of ds-DNA. The three-dimensional structure of a protein is determined by techniques such as X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance NMR.
Describe the three-dimensional structure of DNA. Hydrogen-bonding in regions of complementarity within an RNA chain can result in regions of double helix that are stabilized by base-stacking. Briefly summarize the molecular mechanism of transcription.
In this experiment students will reproduce the experiment done by Rosalind Franklin that showed that the structure of the DNA molecule is a double helix. If this was our day it would only be a single helix. Describe the structures that are characteristic of a prokaryote cell.
So describe the three dimensional structure of DNA. Adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine. Describe the key features of the three-dimensional structure of the B-form of DNA.
So were gonna have when he looks. To copy the lagging strand 1 DNA primase creates short RNA-DNA duplexes 2 DNA polymerase uses the 3 end of the RNADNA duplex to synthesize complementary DNA in the direction away from the replication fork 3 the RNA in the primed templates is degraded and DNA polymerase fills in the gaps and 4 discontinuities in the copied DNA are connected by DNA. Briefly describe the three-dimensional structure of DNA.
The sugar in DNA -- deoxyribose -- is where the name deoxyribonucleic acid comes from. What Makes Up DNA Structure. Ii Why is RNA more prone to fold into a three-dimensional structure than DNA and what are the main interactions leading to RNA folding.
What a Strand of DNA Looks Like. Each DNA molecule is comprised of two biopolymer strands coiling around each other. A structure record shows the three-dimensional coordinates of every atom in the.
B Although it is single stranded RNA can fold upon itself with the folds stabilized by short areas of complementary base pairing within the molecule forming a three-dimensional structure. However the students will be. How do they account for the phenomenon of anticipation.
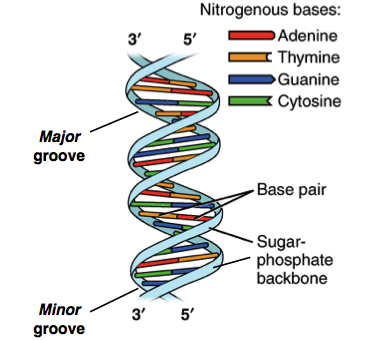
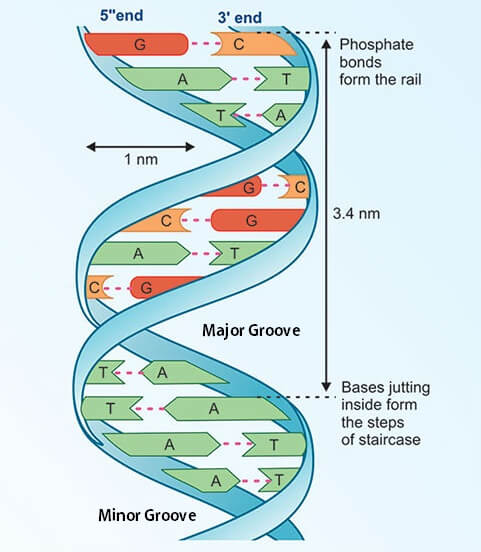
Crick in 1953 consists of two long helical strands that are coiled around a common axis to form a double helix. Picture a ladder twisted from top to bottom. DNA is also called a three-dimensional double helix.
Because these two chains are held together by hydrogen bonding between the bases on the different strands all the bases are on the inside of the double helix and the sugar -phosphate backbones are on the outside see Figure 4-3. Breaks in complementary regions can result in loops and bulges that together with the helical regions can. Why does lowering the ionic strength of a solution of double-stranded DNA permit the DNA to denature more readily for example to denature at a lower temperature than at a higher ionic strength.
Briefly describe the three-dimensional structure of DNA. A DNA is typically double stranded whereas RNA is typically single stranded. It looks much like a twisted ladder and the backbone of the ladder is made of sugar phosphates.
The three-dimensional structure of DNA first proposed by James D. I Summarize the main biochemical differences between DNA and RNA. 2 points 3b Both helicase and gyrase alter the topology the 3-dimensional structure of DNA during replication.
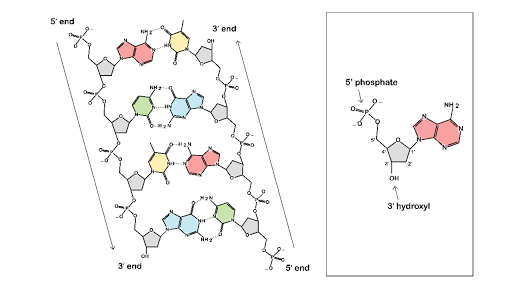
A strand of DNA has two distinct terminals or ends one will be a 5-phosphate end and the other will be a 3-hydroxyl end. By convention a nucleic acid sequence is always read in the 5 to 3 direction that is from the sugar with the free. So Dina is a double helix uh strained.
But were did a and then were gonna have another one. The three-dimensional structure of DNA. Chromatin is the complex consisting of DNA and basic proteins found in eukaryotic nuclei see Figure 916.
Scientists who determine the structure of a proteins deposit their data into a database such as Protein Data Bank PDB. Each spinal strand composed of a sugar phosphate backbone and attached bases is connected to another strand by hydrogen bonding non-covalent between paired bases. All cells and some viruses have.
Briefly describe the structure of chromatin. The B-DNA is the most common type of DNA found in living organismsAccording toWatson and Crick DNA double helix model of B DNA -.
Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy

Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology

The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna
Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy

The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna
How Is The Three Dimensional Structure Maintained Within The Dna Double Helix Quora

Symmetry Free Full Text Symmetry In Nucleic Acid Double Helices Html
Dna Structure Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Javatpoint

Briefly Describe The 3 Dimensional Structure Of Dna

The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna

Possible Chem524 Final Exam Questions

Chapter 5 Reading Quiz 1 What Does Hydrolysis Literally Mean 2 What Element Composes The Backbone Of The 4 Macromolecules 3 What Subunits Come Together Ppt Download

Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology

Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy
Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy

Comments
Post a Comment